The Complete Guide to Six Sigma Belts
Explore the comprehensive guide to Six Sigma Belts, from Yellow to Master Black, understanding their roles in quality management and business improvement.

Six Sigma is a methodology aimed at improving processes by reducing defects and variations. Rooted in data-driven decision-making, it provides a structured approach to identify, analyze, and resolve inefficiencies. The methodology employs tools and techniques such as DMAIC (Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, and Control) for improving existing processes and DMADV (Define, Measure, Analyze, Design, and Verify) for creating new ones. This allows organizations to streamline operations, cut costs, and deliver products and services of higher quality, enhancing customer satisfaction.
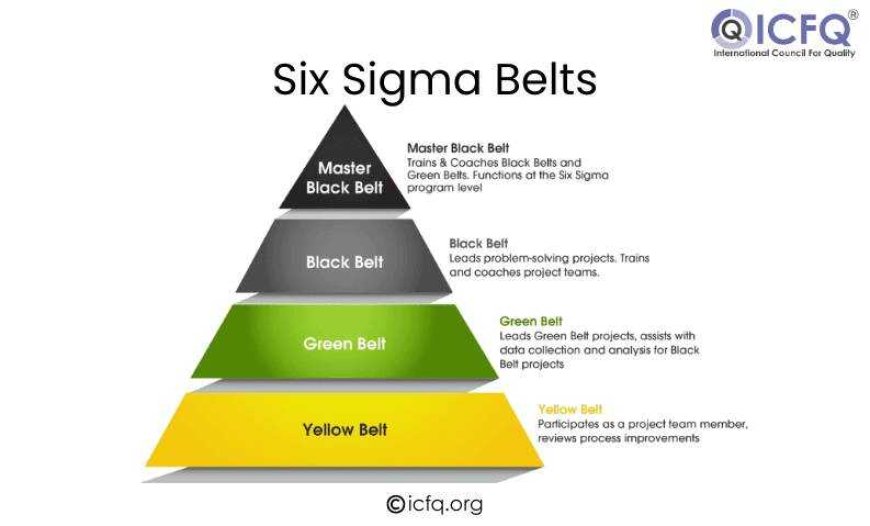
The concept of Six Sigma Belts represents different levels of expertise within the methodology. White belts provide basic support for problem-solving teams, while yellow belts contribute to specific project tasks. Green Belts leads projects of moderate complexity, often under the guidance of Black Belts, who manage larger projects and provide strategic direction. Master Black Belts mentor Black and Green Belts, oversee complex projects, and guide the organization's strategic approach to process improvement. This hierarchical structure ensures that Six Sigma projects are executed effectively, leading to sustainable quality management and continuous process improvements.
Yellow Belt and Key Responsibilities
A Yellow Belt is an entry-level role within the Six Sigma methodology. Individuals in this role possess a foundational understanding of Six Sigma principles and techniques.
There are some of the key responsibilities:
-
Support: Yellow Belts assist Green and Black Belts in their projects, offering basic support for specific tasks.
-
Data Collection: They gather and analyze data pertinent to ongoing projects.
-
Problem Solving: Yellow Belts contribute to problem-solving initiatives, often working on smaller-scale projects or aspects of larger projects.
Contribution to Six Sigma Projects
Yellow Belts play an important role in Six Sigma projects by supporting higher-level Belts in their efforts. They bring foundational knowledge to the table, enabling them to handle specific tasks like data collection, analysis, and preliminary problem-solving. Their involvement ensures a smoother project flow, bridging the gap between team members and management.
Training and Certification Process
To become a Yellow Belt, individuals must undergo formal training. This training covers the basics of Six Sigma methodologies, tools, and techniques, equipping participants with the necessary skills to contribute effectively to projects. After completing the training, candidates must pass a certification exam to demonstrate their proficiency and gain recognition as a certified Yellow Belt. This certification allows them to integrate seamlessly into Six Sigma project teams.
Green Belt
A Green Belt is a mid-level role within the Six Sigma hierarchy, representing someone with a solid understanding of Six Sigma methods and tools. They lead projects of moderate complexity, using statistical analysis and process improvement techniques to streamline workflows. Green Belts also coordinates project teams, guiding them through the DMAIC process and implementing changes to meet project goals.
There are some of the key responsibilities:
-
Project Leadership: Green Belts manages moderate-complexity projects, overseeing tasks from conception to completion.
-
Data Analysis: They gather and analyze data to identify inefficiencies and propose solutions.
-
Team Collaboration: Green Belts coordinates project teams, collaborating with Yellow Belts and other team members to ensure smooth project execution.
-
Implementation: They implement process improvements and monitor their progress to ensure goals are met.
Training, Certification, and Skills Required
To become a Green Belt, individuals must undergo training covering Six Sigma methodologies, tools, and techniques in greater depth. They learn how to manage projects, analyze data, and apply advanced problem-solving strategies. Upon completion of the training, candidates take a certification exam, proving their proficiency and earning recognition as a Green Belt.
Differences between Green Belts and Yellow Belts.
|
Aspect |
Green Belt |
Yellow Belt |
|
Role |
The mid-level role, capable of leading projects |
The entry-level role provides basic support |
|
Project Management |
Leads projects of moderate complexity |
Assists with tasks in smaller-scale projects |
|
Responsibilities |
Analyzes data, implements improvements |
Collects data, supports problem-solving tasks |
|
Leadership |
Manages project teams |
Supports higher-level Belts |
|
Training |
In-depth training in Six Sigma methodologies |
Basic training in Six Sigma principles |
|
Certification |
Requires passing a Green Belt certification exam |
May opt for Yellow Belt certification |
Green Belts typically handle projects such as:
-
Quality Improvement: Enhancing product or service quality through process optimization.
-
Cost Reduction: Identifying inefficiencies in processes to reduce costs.
-
Cycle Time Reduction: Streamlining workflows to shorten the time needed to complete tasks or projects.
Black Belt
A Black Belt in Six Sigma is an advanced role, representing individuals with extensive expertise in Six Sigma methodologies. They are instrumental in leading and driving Six Sigma projects within organizations.
Key Responsibilities and Typical Tasks:
-
Project Leadership: Black Belts lead complex projects from inception to completion, applying advanced statistical analysis and problem-solving techniques.
-
Data Analysis: They gather and analyze data to identify the root causes of issues and develop solutions for process improvements.
-
Mentorship: Black Belts mentor Green and Yellow Belts, guiding them through projects and providing expertise and support.
-
Strategic Planning: They contribute to organizational strategy by aligning Six Sigma initiatives with business goals.
Certification and Advanced Skills
To become a Black Belt, individuals undergo extensive training covering advanced Six Sigma methodologies, statistical analysis, and leadership skills. They must pass a rigorous certification exam to demonstrate their proficiency. Black Belts possess advanced skills in project management, data analysis, and problem-solving, enabling them to drive significant improvements within organizations.
-
Training: Black Belts undergo extensive training sessions focusing on advanced Six Sigma methodologies, statistical analysis techniques, and leadership development.
-
Certification: They must complete a challenging certification exam to validate their proficiency in Six Sigma principles and methodologies.
-
Advanced Skills: Black Belts possess in-depth expertise in project management, utilizing sophisticated statistical tools for data analysis, and employing advanced problem-solving strategies.
-
Expertise Application: Armed with these skills, Black Belts leads initiatives that drive substantial improvements within organizations, optimizing processes and enhancing overall efficiency and quality.
Master Black Belt
Master Black Belts are the highest-ranking Six Sigma experts who lead the strategic planning and vision for Six Sigma within an organization. They focus on big-picture goals and ensure that Six Sigma efforts align with the company's overall objectives. Their role involves guiding other Six Sigma professionals, setting long-term strategies, and identifying areas for improvement to drive organizational success.
Distinction Between Master Black Belts and Other Belts
|
Aspect |
Master Black Belt |
Other Belt Levels |
|---|---|---|
|
Role |
Strategic leadership, shaping Six Sigma strategy |
Project management and implementation |
|
Expertise |
Mastery of advanced Six Sigma methodologies and tools |
Proficiency in specific Six Sigma techniques |
|
Project Involvement |
Provides guidance and oversight for multiple projects |
Leads individual projects and contributes to larger ones |
Strategic Role in Shaping Six Sigma Strategy and Vision
Master Black Belts play a pivotal role in shaping the organization's Six Sigma strategy and vision. They align Six Sigma initiatives with business objectives, identify areas for improvement, and develop long-term strategies for organizational success.
Training and qualifications
-
To become a Master Black Belt, individuals must undergo extensive training in advanced Six Sigma methodologies, leadership development, and strategic planning.
-
Qualifications typically include achieving Black Belt certification and accumulating significant experience in leading complex projects.
Role in Training and Mentoring
-
Master Black Belts serve as mentors and trainers, imparting their knowledge and expertise to other Six Sigma professionals.
-
They play a critical role in developing the skills and capabilities of green, black, and even other master black belts, ensuring the continued growth and success of the organization's Six Sigma initiatives.
each belt in Six Sigma has a crucial role in improving organizations. From Yellow Belts supporting basic tasks to Master Black Belts leading strategic planning, every level contributes to success. As individuals progress, they gain skills to drive improvement and advance their careers. Pursuing Six Sigma training offers a clear path for those wanting to make a difference in process efficiency and career growth. Whether aiming to lead projects or guide strategy, Six Sigma certification opens doors to opportunities in various fields.





























