Key Tools and Techniques for Six Sigma Yellow Belt
Master key tools and techniques for Six Sigma Yellow Belt, including DMAIC and statistical methods, to improve processes and drive ongoing business improvement

Six Sigma is a powerful methodology aimed at improving process efficiency and minimizing defects. While many know of Six Sigma at an advanced level, the foundational skills for newcomers are crucial. One such entry-level certification is the Six Sigma Yellow Belt, which introduces professionals to the basics of Six Sigma and its potential for driving significant business improvements. I will explain the key tools and techniques used by individuals holding a Six Sigma Yellow Belt and how they can contribute to process improvement and organizational success.
Fundamentals of Six Sigma Yellow Belt
The Six Sigma Yellow Belt is an entry-level certification that provides individuals with a foundational knowledge of Six Sigma methodologies. It equips them with the skills to support process improvement efforts under the guidance of Green Belts and Black Belts.
Role & Responsibilities
Yellow Belt professionals play a crucial role in identifying inefficiencies and assisting in process optimization. They act as a bridge between operational teams and senior Six Sigma experts, ensuring smoother implementation of quality management practices.
Key Learning Areas
-
Quality Management: Understanding process improvements
-
Problem-Solving: Identifying and addressing inefficiencies
-
Basic Statistical Analysis: Using data to drive decisions
The Core of Six Sigma Problem Solving
One of the most important techniques for a Six Sigma Yellow Belt to master is the DMAIC framework. DMAIC stands for Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, and Control. It is the roadmap used in Six Sigma projects to ensure that problems are effectively identified, measured, analyzed, and solved, with sustainable improvements in place.
-
Define: This is the first step where the problem is defined. The project goals, customer needs, and project scope are all outlined.
-
Measure: In this phase, data is collected to measure the current process performance. The focus is on understanding the process and identifying any existing issues.
-
Analyze: This phase involves analyzing the collected data to identify root causes of problems and variations in the process.
-
Improve: Once the causes are understood, solutions are designed and implemented to address the issues and improve process performance.
-
Control: Finally, the improvements are standardized, and controls are put in place to maintain the gains.
For Six Sigma Yellow Belts, learning how to use this framework effectively is key to contributing to process improvement efforts.
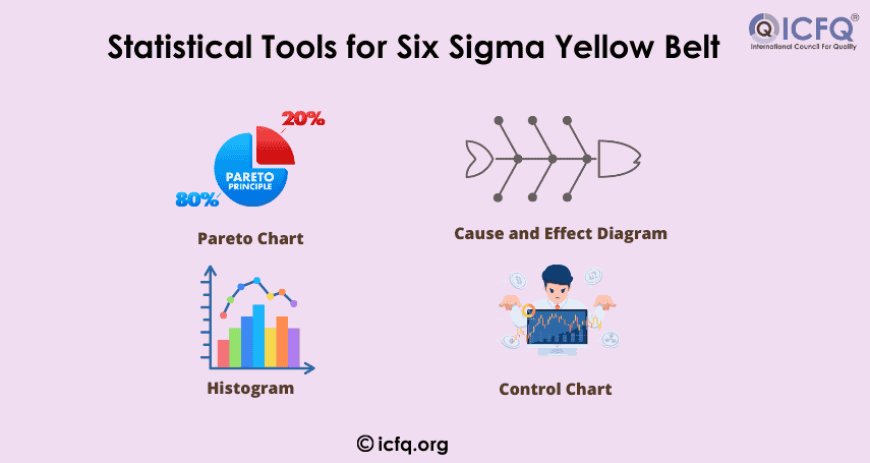
Basic Statistical Tools for Six Sigma Yellow Belt Professionals
In addition to the DMAIC framework, Six Sigma Yellow Belts are introduced to several fundamental statistical tools to help them analyze data and make informed decisions. These tools are designed to identify patterns, reduce variations, and improve process efficiency.
Some of the key statistical tools that Six Sigma Yellow Belt professionals use include:
-
Pareto Chart: The Pareto Chart is a simple yet effective tool used to prioritize problems based on their frequency or significance. It follows the 80/20 rule, which states that 80% of the problems are caused by 20% of the issues. By focusing on the most impactful problems, Yellow Belt professionals can contribute to meaningful improvements.
-
Cause and Effect Diagram (Fishbone Diagram): This tool helps identify the root causes of a problem by visually mapping out the potential causes in categories like people, processes, equipment, and materials. By using a cause-and-effect diagram, Yellow Belt professionals can start looking beyond surface-level symptoms to uncover the true drivers of process inefficiency.
-
Histogram: A histogram is a type of bar graph used to represent the distribution of data points. It helps Yellow Belt professionals see trends and patterns in the data, making it easier to spot irregularities or areas for improvement.
-
Control Chart: A control chart is used to monitor process stability over time. It helps detect whether a process is in control or whether there are significant variations that require attention. For Yellow Belt professionals, control charts offer a simple way to track performance metrics and identify when interventions are needed.
Collaboration and Communication Skills for Six Sigma Yellow Belts
Although technical tools and methods are essential, the success of any Six Sigma initiative also depends on effective teamwork and communication. Six Sigma Yellow Belts often work in teams with Green Belts, Black Belts, and process owners. Therefore, developing strong collaboration and communication skills is critical.
-
Teamwork: Six Sigma projects require cross-functional teams, and Yellow Belt professionals often act as vital contributors. They must be comfortable working in groups and understanding how their role fits into the bigger picture.
-
Communication: Yellow Belts must be able to communicate effectively with both technical and non-technical stakeholders. Whether it's presenting data findings, explaining improvements, or raising concerns, clear communication is essential to ensuring that everyone involved is aligned.
-
Problem-solving: At the core of Six Sigma lies problem-solving, and Yellow Belts are often tasked with identifying issues, gathering data, and working with the team to propose solutions. Having an analytical mindset is key for finding practical, data-driven solutions.
How Six Sigma Yellow Belts Contribute to Organizational Success
Though Six Sigma Yellow Belts may not be in charge of overseeing large-scale projects, their contributions can significantly impact an organization’s overall performance. By understanding basic Six Sigma tools, techniques, and methodologies, Yellow Belt professionals can help teams identify inefficiencies, improve processes, and drive continuous improvement within their respective departments or units.
As the entry-level certification for Six Sigma, the Yellow Belt provides professionals with a solid foundation to grow in the field of quality management. It opens doors for them to take on more significant responsibilities, pursue higher-level certifications (such as Green Belt or Black Belt), and eventually become key players in larger, more complex Six Sigma initiatives.
Six Sigma Yellow Belt certification is a great starting point for those looking to make an impact in process improvement and quality management. By mastering key tools such as the DMAIC framework, statistical tools, and effective communication skills, Yellow Belt professionals can significantly contribute to the improvement of processes within their organization. Though they may start at an entry-level, their expertise in these tools and techniques sets the stage for continuous professional growth, making them valuable assets in any Six Sigma project.
As businesses continue to adopt Six Sigma principles, those with a Six Sigma Yellow Belt will be well-positioned to support improvements, drive change, and contribute to organizational success.





























